U.S. 10-Year Bond Yield: Trends, Impact on India, and Future Outlook
The U.S. 10-year bond yield is a critical indicator of global financial health, influencing interest rates, investor sentiment, and economic stability worldwide. From its historical trends to the latest developments, understanding this metric helps investors and policymakers gauge the trajectory of the global economy.
Key Highlights of the U.S. 10-Year Bond Yield
The U.S. core inflation rate for December stood at 3.2% year-over-year, slightly lower than the estimated 3.3%. This positive deviation reflects easing inflation pressures in the U.S. economy.
Following this inflation report, the U.S. 10-year bond yield declined from 4.7% to 4.6%, signaling optimism in the financial markets. This decline is particularly significant for emerging markets, including India, as it may reduce Foreign Institutional Investor (FII) selling pressures if the trend persists.
Historical Trends in the 10-Year Bond Yield (2010-2025)
Below is a chart showcasing the U.S. 10-Year Bond Yield trends from 2010 to 2025, including key events like the pandemic and subsequent recovery:
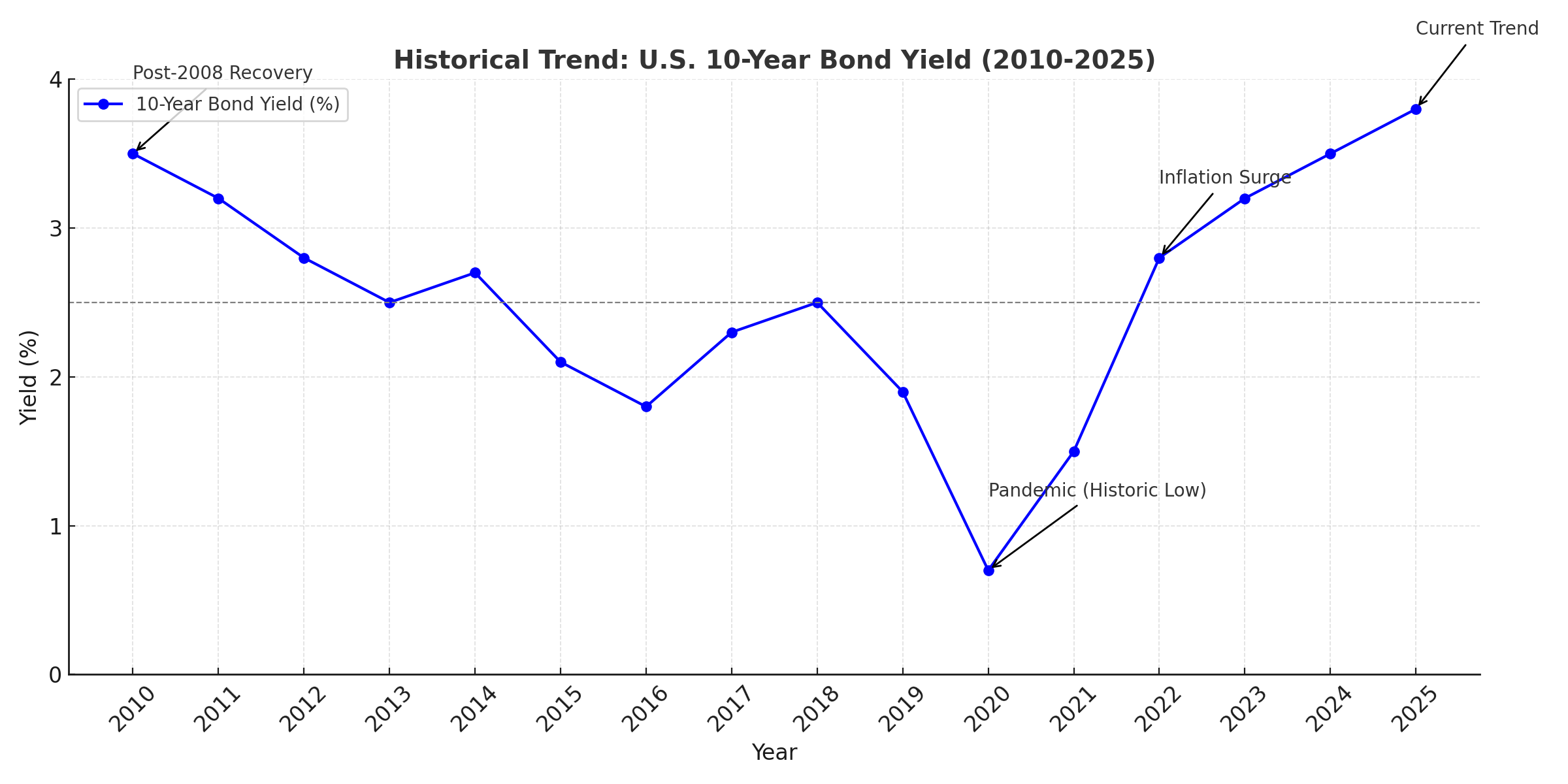
A closer look at the historical trend of the 10-year yield reveals several pivotal moments:
- 2010-2012: Yields remained subdued following the 2008 global financial crisis.
- 2013: The “taper tantrum” caused a spike as the Federal Reserve announced plans to reduce quantitative easing.
- 2020: The pandemic caused yields to plummet to historic lows near 0.5% as investors sought safe-haven assets.
- 2021-2023: Yields steadily climbed, peaking at 4.7% due to aggressive Fed rate hikes to combat inflation.
- 2025: The downward trend observed now hints at potential market stabilization.
Impact on the Indian Market
The decline in the U.S. bond yield has direct implications for emerging economies like India:
- Reduced FII Selling: Lower U.S. yields make Indian equities and debt markets more attractive, encouraging foreign inflows.
- Stable Rupee: Reduced outflows help stabilize the Indian currency, improving the trade deficit.
- Borrowing Costs: Lower U.S. yields often ease pressure on Indian government bond yields, potentially reducing borrowing costs domestically.
What Lies Ahead?
As the U.S. 10-year bond yield exhibits a slight decline, investors are closely monitoring the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy stance. Additionally, the global economic landscape is likely to shift next week as Donald Trump assumes the U.S. presidency. This political transition could further influence market sentiment and bond yields.
Conclusion
The U.S. 10-year bond yield is a linchpin in the global financial system, reflecting economic trends and shaping market dynamics. With recent data signaling a decline in yields, the outlook appears favorable for emerging markets, including India. However, investors must stay vigilant as geopolitical and economic events unfold in the coming weeks.
References:
- U.S. Treasury Department: Treasury Yields
- Federal Reserve: Interest Rate Policies
Internal Link:
Learn how financial metrics like Q-Square Analysis shape investment decisions.
External Link:
Stay updated with live yield data at MarketWatch.


Nice article